Can You MIG Weld Stainless Steel without Shielding Gas
Aug 28th 2023
What Is Shielding Gas?
Shielding gas is a type of gas used in welding to protect the metal being welded from the atmosphere. It creates a barrier around the welding area to prevent the metal from reacting with oxygen, nitrogen, and other gases in the air, which can cause problems like rust and weak welds. For MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, also known as GMAW (Gas Metal Arc Welding), shielding gas is directed around the arc and the molten weld pool to create a protective barrier, which helps to produce a clean and stable environment for the welding process.
Typically composed of inert gases like argon or helium (or a mixture of these gases), shielding gas is introduced to the welding area to displace the ambient air. This inert gas shield prevents the oxidation of the metal by creating a controlled environment with minimal oxygen and nitrogen content.
Each type of shielding gas comes with its own set of pros and cons, and most welding jobs require at least some mixture of two or more types of gases. For example, in order to obtain high-quality weld results, a combination of about 75-95% argon and 25-5% carbon dioxide is typically employed. The choice of which to use heavily depends on a number of factors, including welding position, welding process, material thickness, project requirements, aesthetics, and costs.
Let's take a quick look at how each type of shielding gas compares to each other.
| Shielding Gas Type | Pros | Cons |
| Argon |
|
|
| Helium |
|
|
| Carbon Dioxide |
|
|
| Argon-Carbon Dioxide Mix |
|
|
| Tri-Mix (Helium, Argon, Carbon Dioxide) |
|
|
How Is Shielding Gas Used for MIG Welding Stainless Steel?
When MIG welding stainless steel, shielding gas helps preserve the integrity of the metal's corrosion-resistant properties and prevents defects such as porosity, excessive spatter, and poor weld quality. The presence of shielding gas is particularly helpful due to the stainless steel’s susceptibility to oxidation and contamination at high temperatures.
Stainless steel contains chromium, which forms a thin, protective oxide layer on its surface that provides corrosion resistance. However, during welding, high temperatures can disrupt this oxide layer, making the stainless steel vulnerable to oxygen and nitrogen in the air. This can lead to a phenomenon known as "weld decay" or "sensitization" where the material loses its corrosion resistance in the heat-affected zone.
In addition to preventing oxidation, shielding gas also affects the stability of the welding arc. By stabilizing the electric arc between the welding wire and the workpiece, shielding gas can further improve control over the welding process. The specific choice of shielding gas depends on various factors, including the type of stainless steel being welded, the welding position, and the desired characteristics of the weld.
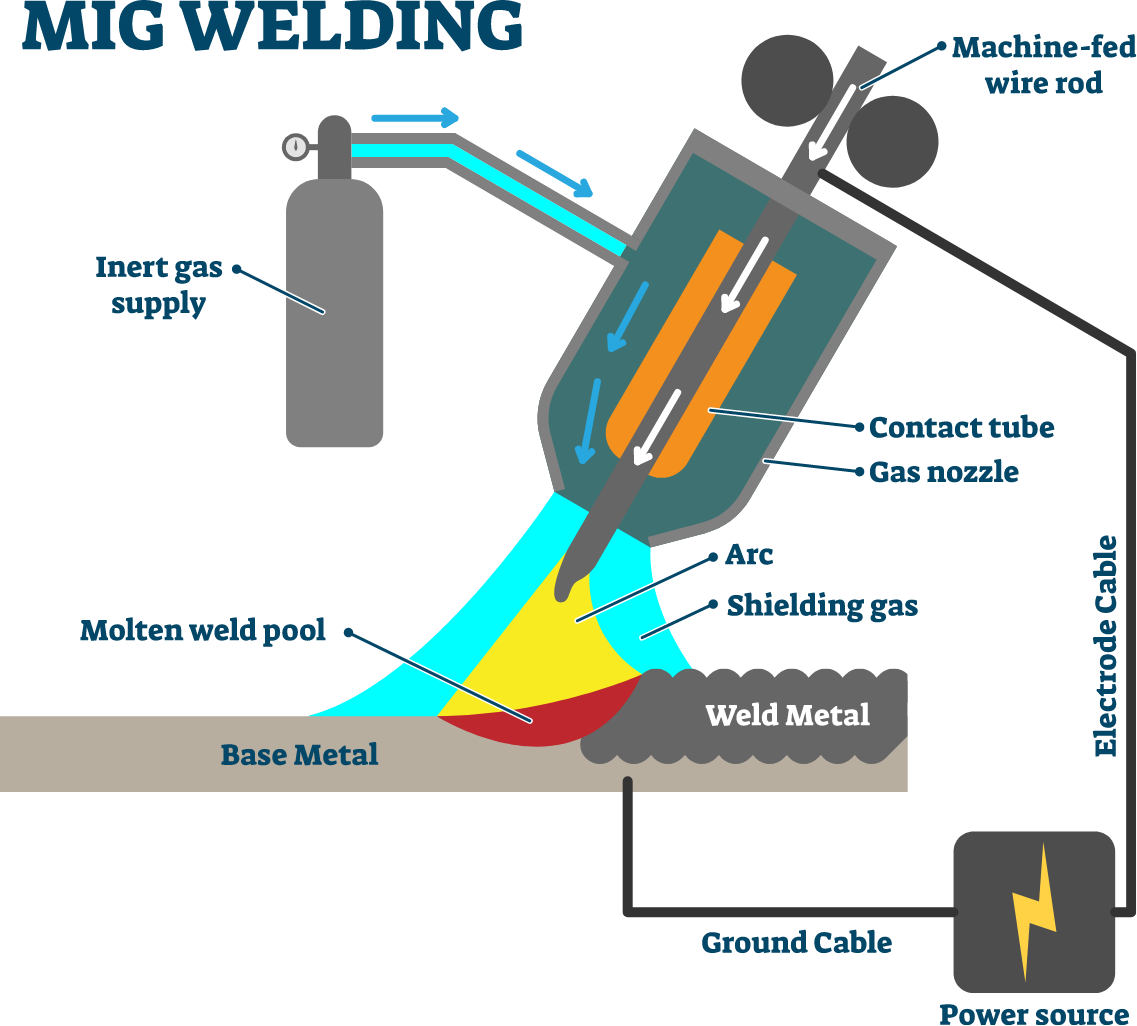
Is MIG Welding Stainless Steel Without Shielding Gas Recommended?
It's not advisable to MIG weld stainless steel without the use of shielding gas. While it's technically possible to weld stainless steel without shielding gas by employing self-shielded flux-cored arc welding wire (FCAW), completely abandoning the use of shielding gas altogether is discouraged. This is especially true with stainless steel due to its distinctive characteristics, including its high heat retention properties. It's highly recommended to opt for shielding gas when MIG welding stainless steel or any other type of material for optimal results and the longevity of the welded joints.
Self-shielding flux-cored welding wires, unlike their counterparts, gas-shielded flux-cored welding wires, utilize their flux core to generate a certain level of protection. The flux in the wire melts and creates a gaseous shield around the weld pool, which protects it from contaminants and oxidation. A slag layer, which needs to be removed post-weld, forms on the weld as it cools, which traps the weld and further protects it from the atmosphere.
Self-shielded flux-cored welding wires are incredibly useful for welding on most materials; however, given the finicky nature of stainless steel, this method may not provide sufficient shielding to counteract the challenges posed by distinctive characteristics of this type of material.
Opting for shielding gas when MIG welding stainless steel is highly recommended to ensure optimal results, minimize the risk of defects, and promote the longevity of the welded joints. Stainless steel is a sensitive material to weld, so a welder should always opt for a welding method that preserves the corrosion-resistant characteristics of stainless steel to high-quality, durable welds.

Shielding Gas Tips for MIG Welding Stainless Steel
Below we’ll tackle various tips that can help you make the most of your stainless steel welding project. Remember: The right shielding gas selection and proper post-weld practices are vital for achieving quality and rust-free welds in stainless steel.

Shielding Gas Tips for Stainless Steel FCAW
As previously mentioned, some self-shielded flux-cored wires may not require shielding gas when working with other types of base materials, but shielding gas is essential for stainless steel due to the metal’s unique properties. By utilizing proper shielding gas mixtures and procedures during stainless steel flux-cored arc welding, quality end results are more likely to occur.
Choosing the Right Shielding Gas for Stainless Steel FCAW
- When utilizing flux-cored wire that doesn't have self-shielding properties, it's crucial to have the appropriate shielding gas mixture on hand.
- For dual shield flux-cored wires, common options include 100% carbon dioxide or a mixture of 75% argon and 25% carbon dioxide.
- It's advisable to seek guidance from your welding wire manufacturer to receive specific mixture recommendations based on the stainless steel alloy and thickness.
Post-Weld Shielding Gas with Flux-Cored Wire Tips
- Due to the increased production of slag and by-products during flux-cored welding, the implementation of post-weld shielding gas is important.
- Ensure the maintenance of post-weld shielding gas coverage for a few seconds to mitigate the formation of potential defects, such as porosity or excessive oxidation.
FAQs on Shielding Gas for MIG Welding Stainless Steel Applications
To summarize our discussion on the necessity of using shielding gases for MIG welding stainless steel, let's explore some of the most frequently asked questions that many welders commonly encounter.
Can I MIG weld stainless steel without shielding gas?
As we've discussed so far, it is technically possible by utilizing self-shielded flux-cored welding wire, but it's highly unadvisable. It would be incredibly challenging to achieve a high-quality weld due to stainless steel's high susceptibility to oxidation and contamination. We recommend always using the right mix of shielding gas for optimal results and reliably strong weld joints.
What shielding gas is best for MIG welding stainless steel?
The exact choice of shielding gas highly depends on several factors, but we generally recommend considering a suitable mixture of argon and carbon dioxide or with helium added in. It's best to avoid using 100% argon or helium as these are inert gases. Make sure that you consider the type of stainless steel, welding position, and project requirements.
How do I set the shielding gas flow rate for stainless steel MIG welding?
The flow rate needs to be calibrated based on your welding machine manual or relevant charts. While a starting point could be around 35 cubic feet per hour (CFH), customization for specific applications may be necessary. Make sure that you watch for excessive flow rates, as too much gas can lead to weld quality concerns.
How can I prevent common issues like porosity and excessive spatter in stainless steel MIG welding?
Welding defects such as porosity, excessive spatter, cracking, and distortion are common when there's inadequate gas coverage. It is incredibly important to correctly set the gas flow rate and select the appropriate gas mixture that suits the current project. It is also very important to maintain consistent gas flow throughout the welding operation.
Explore NS ARC Stainless-Steel Welding Wires
Are you looking for a quality stainless-steel welding wire for your next project? When delving into the realm of MIG welding stainless steel, NS ARC Satin Glide® stainless-steel welding wire stands as the ultimate companion. Its performance in corrosion resistance guarantees welds that endure even the harshest environments, ensuring long-lasting and robust results.
With exceptional weld strength and the ability to withstand high temperatures, the integrity and dependability of your welded joints remain uncompromised. This versatile welding wire offers a user-friendly experience and adapts seamlessly to a wide range of tasks, from joining to modification and repair.
Moreover, Satin Glide® stainless-steel welding wire seamlessly integrates with mechanized, robotic, and semi-automatic welding methods, streamlining your welding processes for optimal efficiency and precision. In delivering the Satin Glide® solution, NS ARC presents a premium choice that not only guarantees exceptional weld performance but also aligns with the highest standards of quality and reliability.
Check out our collection of stainless-steel welding wires and learn more about how their strength and corrosion resistance can enhance your next welding adventure.
DISCLAIMER: This information is descriptive in nature and not purely prescriptive. Refer to your own welding machine’s user manual for proper settings and consult a welding expert for support.



